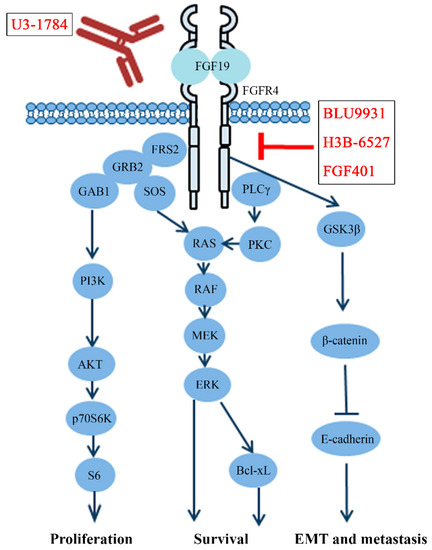
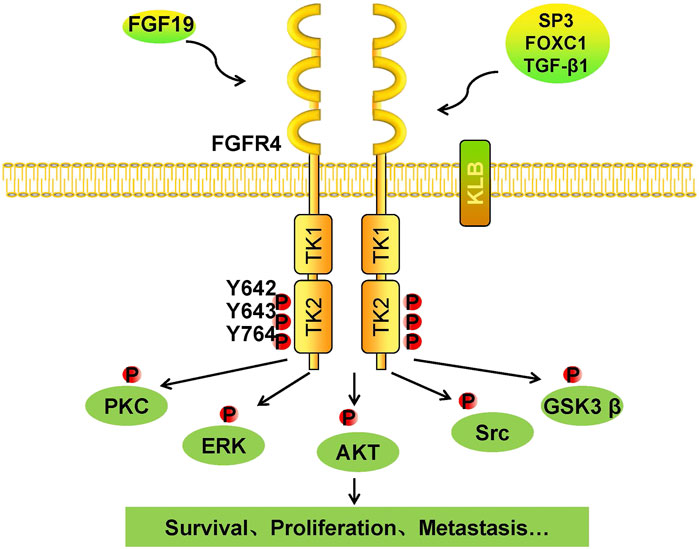
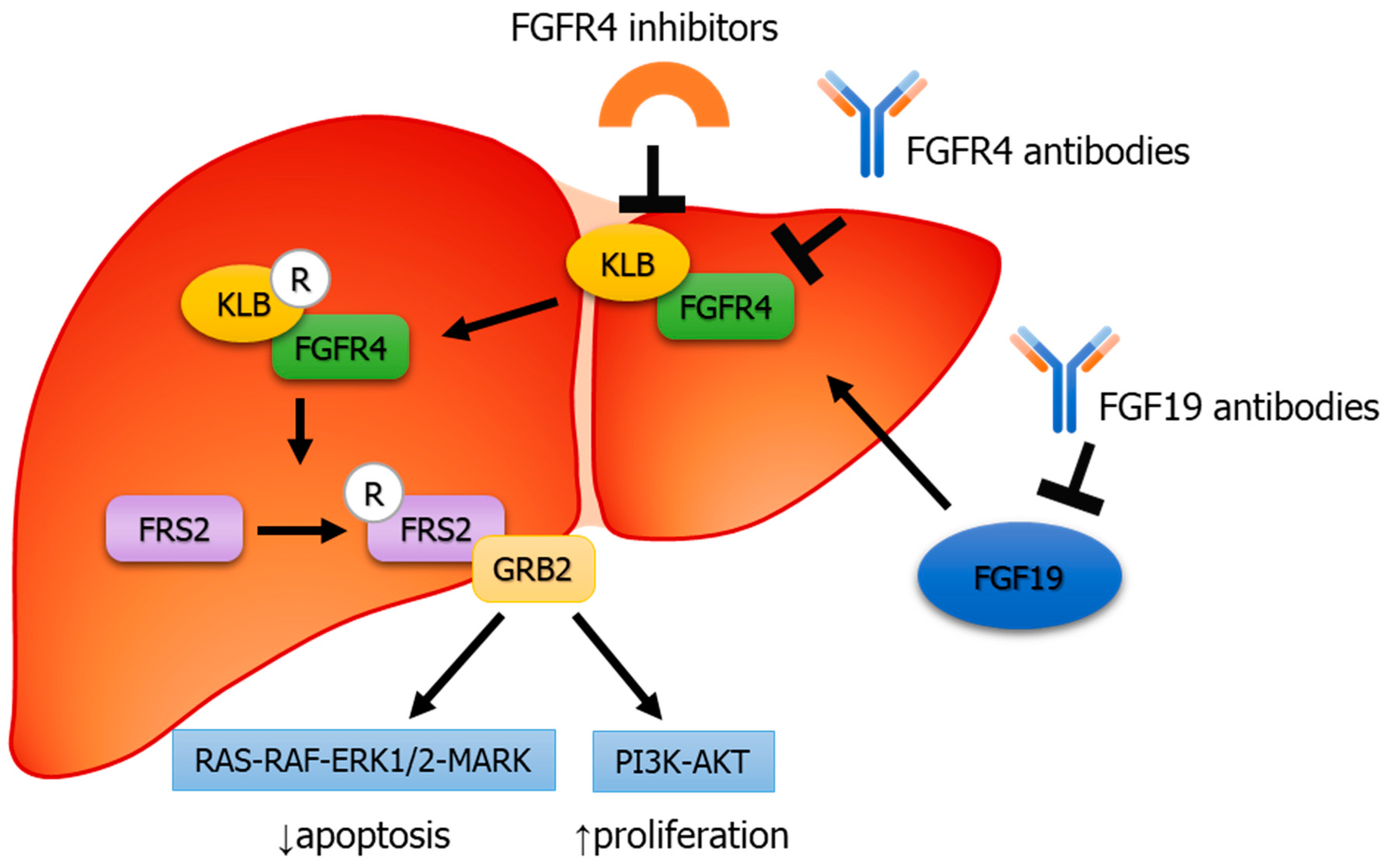
Schematic representation of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling pathway involves in... | Download Scientific Diagram

FGF19 amplification reveals an oncogenic dependency upon autocrine FGF19/FGFR4 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Oncogene
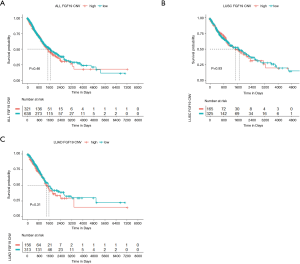
Enhanced expression of FGF19 predicts poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer - Chen - Journal of Thoracic Disease
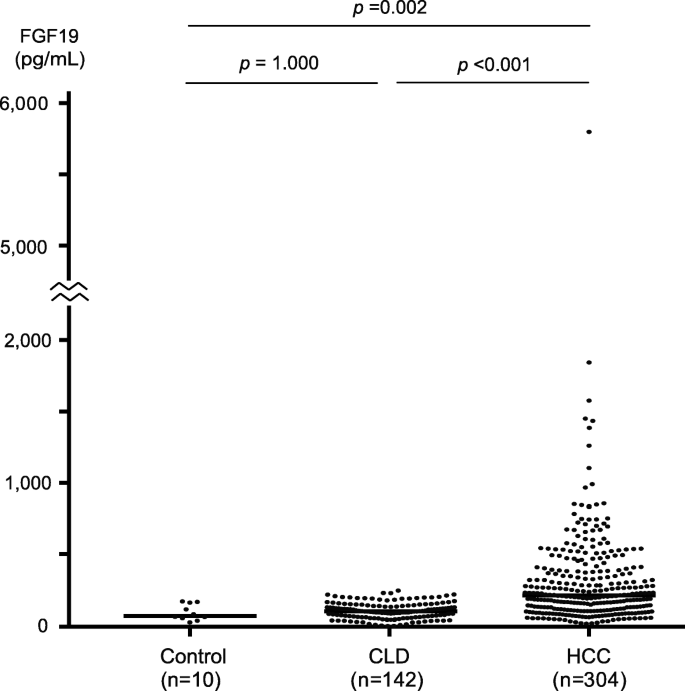
Serum fibroblast growth factor 19 serves as a potential novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma | BMC Cancer | Full Text

FGF19 and its analog Aldafermin cooperate with MYC to induce aggressive hepatocarcinogenesis | EMBO Molecular Medicine
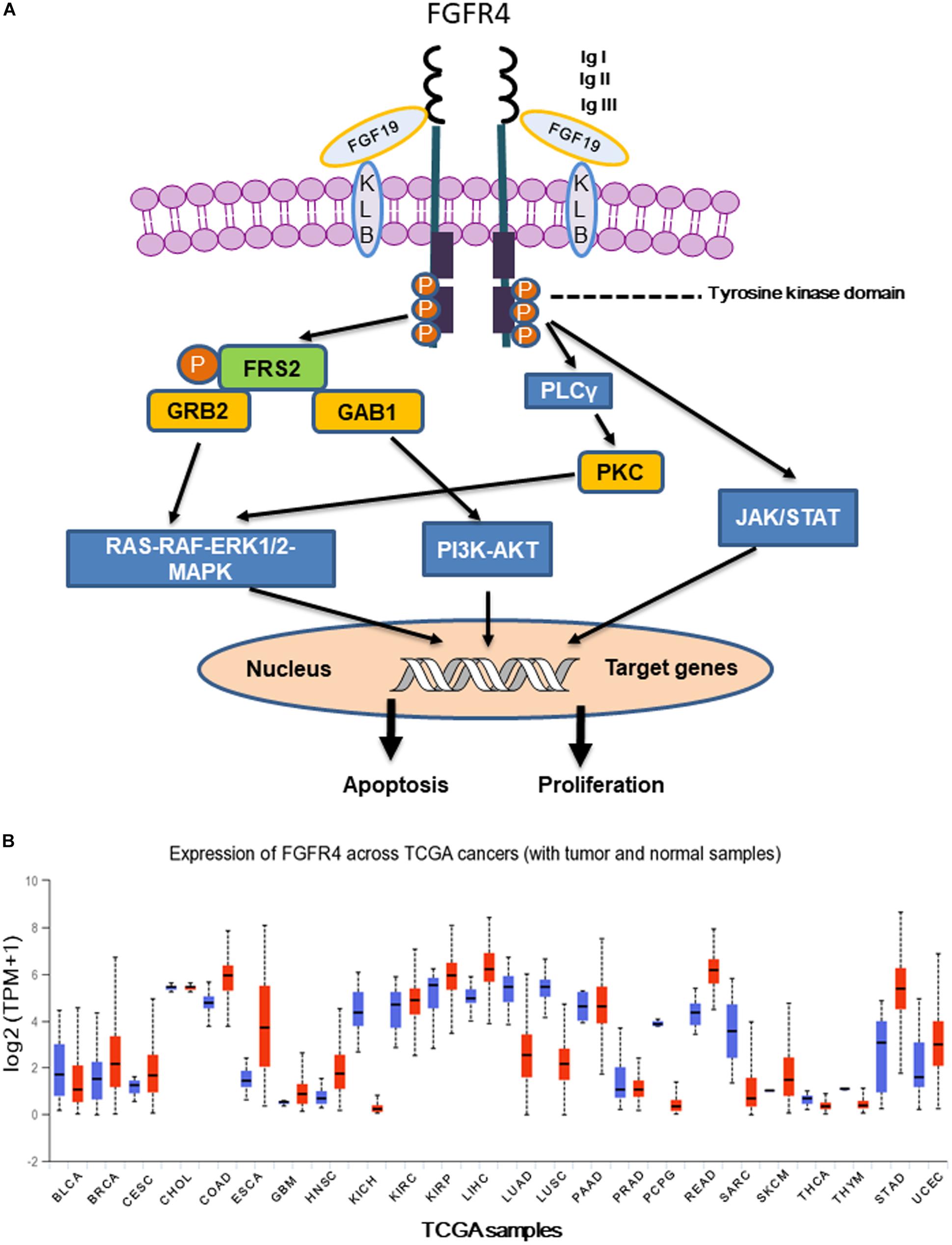
Frontiers | Dissecting the Role of the FGF19-FGFR4 Signaling Pathway in Cancer Development and Progression

FGF19 amplification reveals an oncogenic dependency upon autocrine FGF19/FGFR4 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Oncogene
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) and fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) autocrine enhance breast cancer cells survival | Oncotarget

FXR-FGF19 signaling in the gut–liver axis is dysregulated in patients with cirrhosis and correlates with impaired intestinal defence | Hepatology International

In vitro assays of FGF19-stimulated HCC cells. (A) Proliferation of HCC... | Download Scientific Diagram
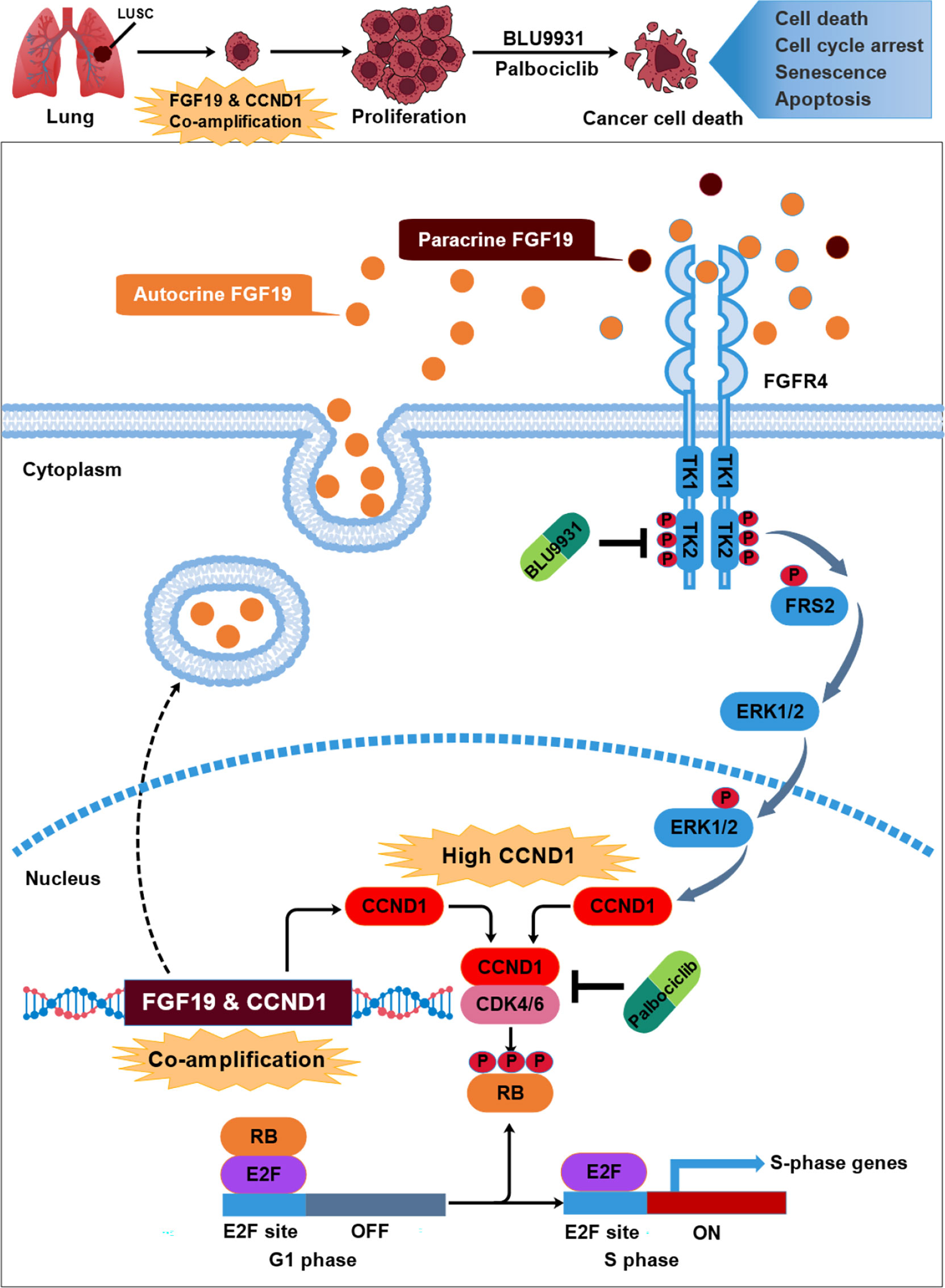
Frontiers | FGF19 Is Coamplified With CCND1 to Promote Proliferation in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Combined Inhibition Shows Improved Efficacy

Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 Targeting in Cancer: New Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. - Abstract - Europe PMC

FGF19 amplification reveals an oncogenic dependency upon autocrine FGF19/FGFR4 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Oncogene

The impact of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling inhibition in antitumor activity of multi-kinase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma | Scientific Reports

FGF19 and FGF21 for the Treatment of NASH—Two Sides of the Same Coin? Differential and Overlapping Effects of FGF19 and FGF21 From Mice to Human | Semantic Scholar
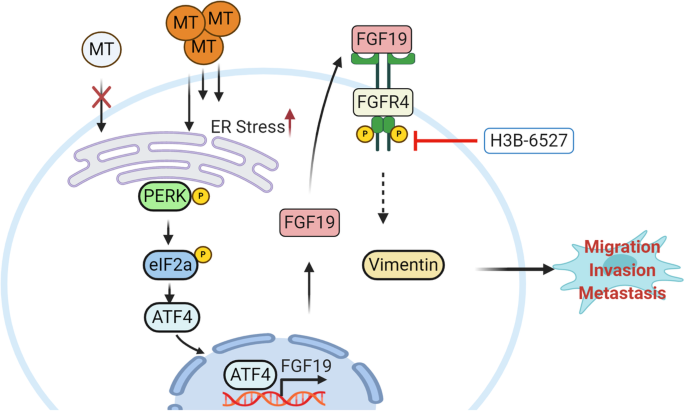
FGF19/FGFR4 signaling axis confines and switches the role of melatonin in head and neck cancer metastasis | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text
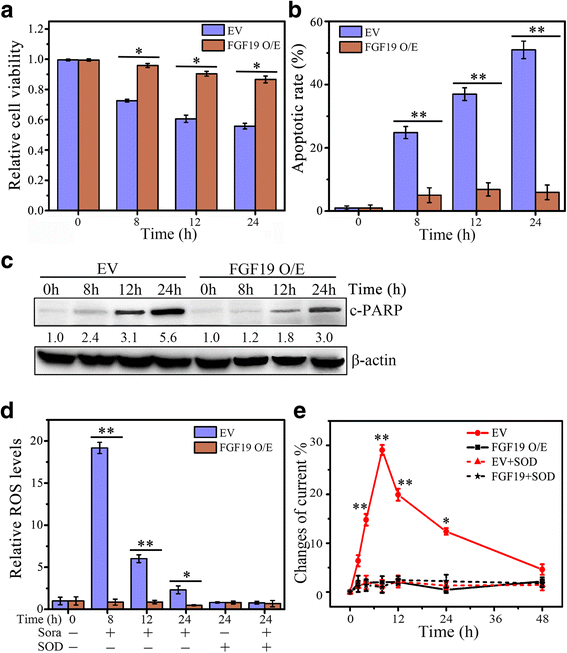
FGF19/FGFR4 signaling contributes to the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text

Targeted inhibition of FGF19/FGFR cascade improves antitumor immunity and response rate in hepatocellular carcinoma | Hepatology International
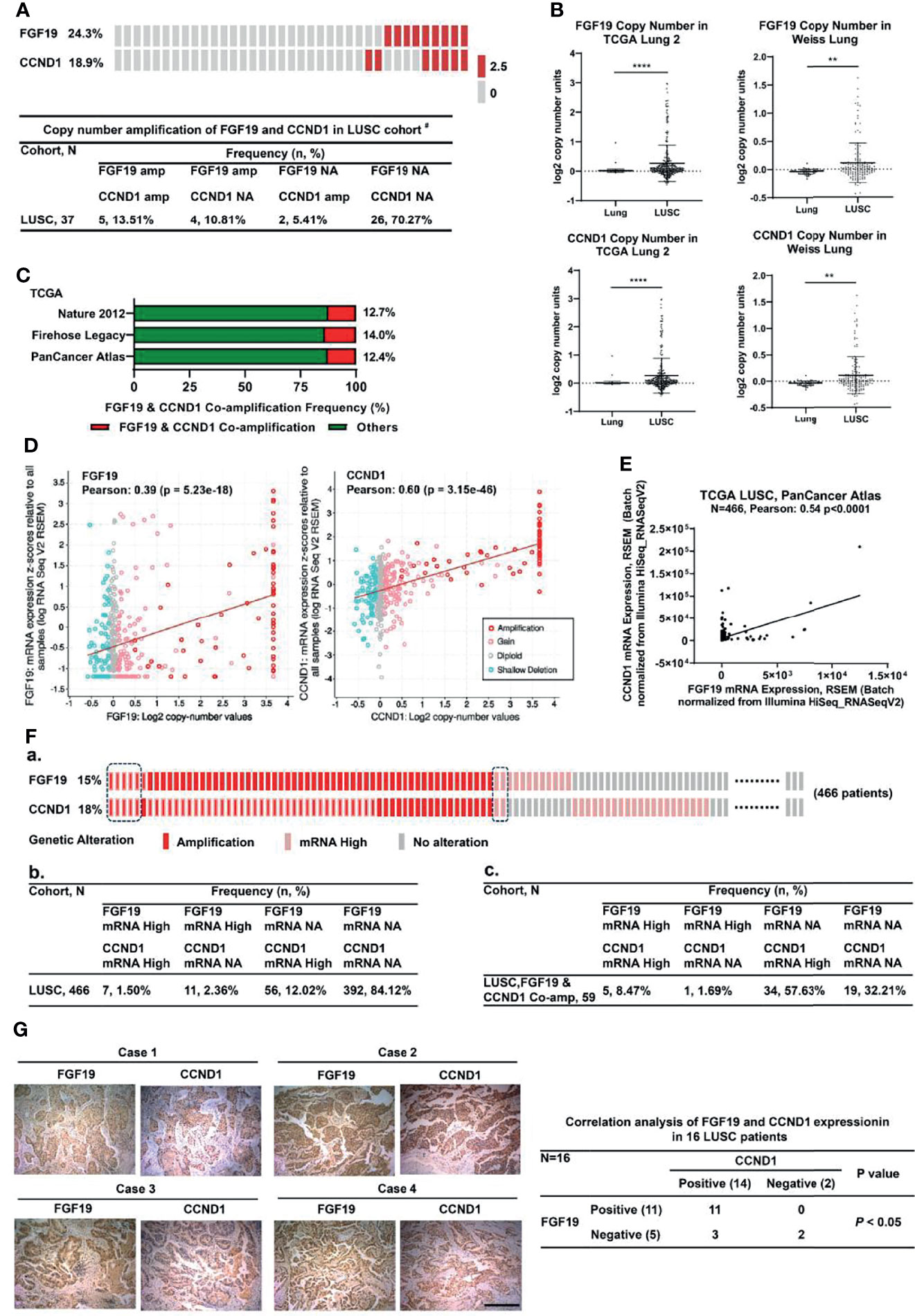
Frontiers | FGF19 Is Coamplified With CCND1 to Promote Proliferation in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Combined Inhibition Shows Improved Efficacy